PLDYNA calculates very accurately the required roller elevations and orientations. The calculation of the contact point between a roller and the pipe at any point along the pipeline and at different time steps in dynamic analysis cases requires consideration of roller type, roller orientation, roller radius, pipe radius, and exact pipe geometry. PLDYN can accurately perform these necessary calculations for two types of rollers. Fixed rollers are typically mounted on a support fixed to the stinger section. The orientation and position of the fixed rollers remain fixed in the local stinger section coordinates but can move with the motion of the stinger section. The second kind of roller PLDYNA can model are hinged rollers which is typically a series of rollers mounted on a box structure attached the stinger section by a hinge which allows rotation of the roller box.
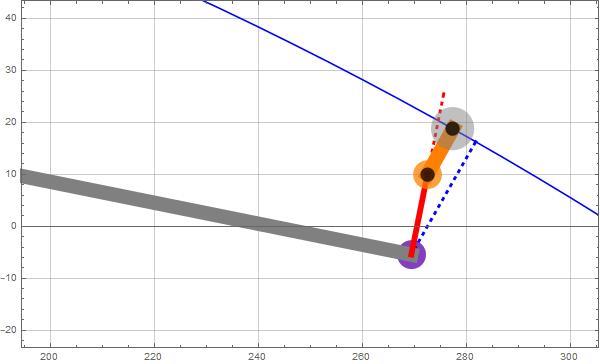
When rollers contact the pipe, the roller box assembly aligns with the pipe direction ensuring that plane containing roller axes remain parallel to the pipe axis (blue). It is therefore necessary to calculate the roller orientation during the analysis. Figure 5 only shows the middle roller which remains in the plane perpendicular to the pipe and passing through the roller box hinge.
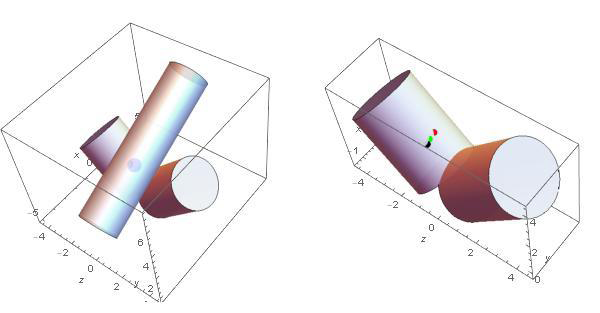
PLDYN calculates the central roller contact point and also determines the roller support (shown in red) height and orientation in local stinger section coordinates. Modelling central roller only provides a good approximation to the hinged roller boxes. There are several reasons for this. Firstly, since the actual pipe geometry (curvature) is determined during the analysis and changes along the overband and time steps, it is not practical to adjust roller profile to match the pipe profile in advance. Secondly, it is not practical to calculate the true loads on individual rollers as the structural behavior of the roller box and the stinger under the actual loads is not feasible in most circumstances. It is beyond the scope of PLDYNA software to incorporate the structural response of roller box assembly and the stinger sections. In any case, the load distribution across the rollers on the same roller box would be much smaller than the average load unless the roller box assembly is rigid in which case it is more likely that the pipe would only touch the most extreme two rollers.
